Dental crowns, commonly known as dental caps, are invaluable restorations for rebuilding damaged or decayed teeth. These restorations offer both strength and aesthetic benefits, making them a popular choice among patients seeking to regain their confident smiles. However, in some cases, individuals may be left with a “black border” at the gumline of their crowns.
This disheartening occurrence manifests as a noticeable dark line where the crown meets the gum tissue. In our comprehensive guide, we will explore the reasons behind this unsettling phenomenon and shed light on the various professional prosthodontic solutions to rectify this problem. Akin to flipping a before-and-after switch, the transformation achieved by addressing black borders can be remarkable.
A black border at the gumline does not merely affect the visual appeal of your smile; it can also signify underlying dental concerns. Neglecting this issue may lead to gum health problems and jeopardize the longevity of your dental restoration. It is essential to understand the root causes, the diagnostic process, and the treatment options available to correct black borders.
Join us as we explore the intricacies of black borders on dental crowns and explore real-life, transformative before-and-after scenarios guided by the expertise of our prosthodontist. Read on to learn more!
Causes of Black Borders
Poor Marginal Fit

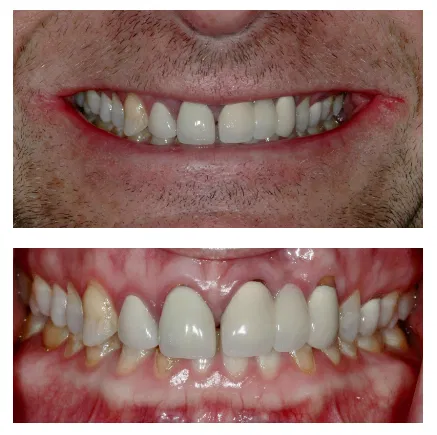
- Patient-specific Fitting: Each patient’s dental anatomy is unique. If a crown is not custom-fitted accurately to the patient’s tooth, it can create gaps where bacteria can infiltrate. Over time, this poor marginal fit can lead to the development of a black border. See the black border in the picture above.

- Inadequate Restoration: Insufficiently sealed margins between the crown and the tooth can allow oral fluids and debris to penetrate, causing discoloration and decay. Ensuring a precise, snug fit is essential to prevent black borders.
Gum Recession

- Natural Aging Process: As patients age, gum recession is a common occurrence. Receding gums expose the underlying tooth structure and the crown’s margin, which can create the appearance of a black border. See picture above.
- Periodontal Conditions: Certain gum diseases and conditions can accelerate gum recession. Patients with periodontal issues are more susceptible to black borders around their crowns.
Aging Crowns
- Wear and Tear: Older dental crowns can deteriorate over time due to wear and chipping. As the crown ages, the materials used may degrade, leading to the emergence of black borders.
- Outdated Materials: Older crown materials may be more prone to developing black borders. This is due to the metal that shows at the border of the crown at the gum line. We no longer use dark metals in crown restorations, which greatly improves the dental aesthetics of the crown.
Understanding these causes is the first step towards effectively addressing and resolving black border issues in dental crown patients.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Clinical Examination
- Visual Inspection: A skilled prosthodontist conducts a thorough visual examination of the patient’s oral cavity. This examination includes scrutinizing the crown’s margin, gumline, and adjacent teeth to identify any black border or related issues.
- Checking Fit: The prosthodontist may use an explorer to assess the crown’s fit and check for any irregularities along the gumline. The periodontal health around the tooth will also be determined and periodontal probe will be used to check for any deep pockets.
X-rays and Imaging
- X-rays: Dental X-rays are essential for a comprehensive assessment. They provide insight into the crown’s fit. X-rays can show gaps or open margins where the crown meets the tooth. X-rays also show the health of the root and any periodontal bone loss.
- Intraoral Scans: 3D intraoral scans are now used instead of uncomfortable impression materials. These scans create precise 3D images, allowing prosthodontists to visualize the shape of the crown and to evaluate the occlusion or biting surfaces.
Treatment Planning
- Customized Solutions: Based on the clinical examination and imaging results, the prosthodontist develops a personalized treatment plan. This plan outlines the most suitable method to address the black border, taking into account the patient’s specific case.
- Discussion with the Patient: The prosthodontist communicates the diagnosis and treatment options to the patient, ensuring they understand the recommended course of action and actively participate in decision-making.
A meticulous diagnosis and evaluation process is vital for successfully identifying the causes of black borders and determining the most effective treatment strategy for each patient.
Treatment Options
Crown Replacement

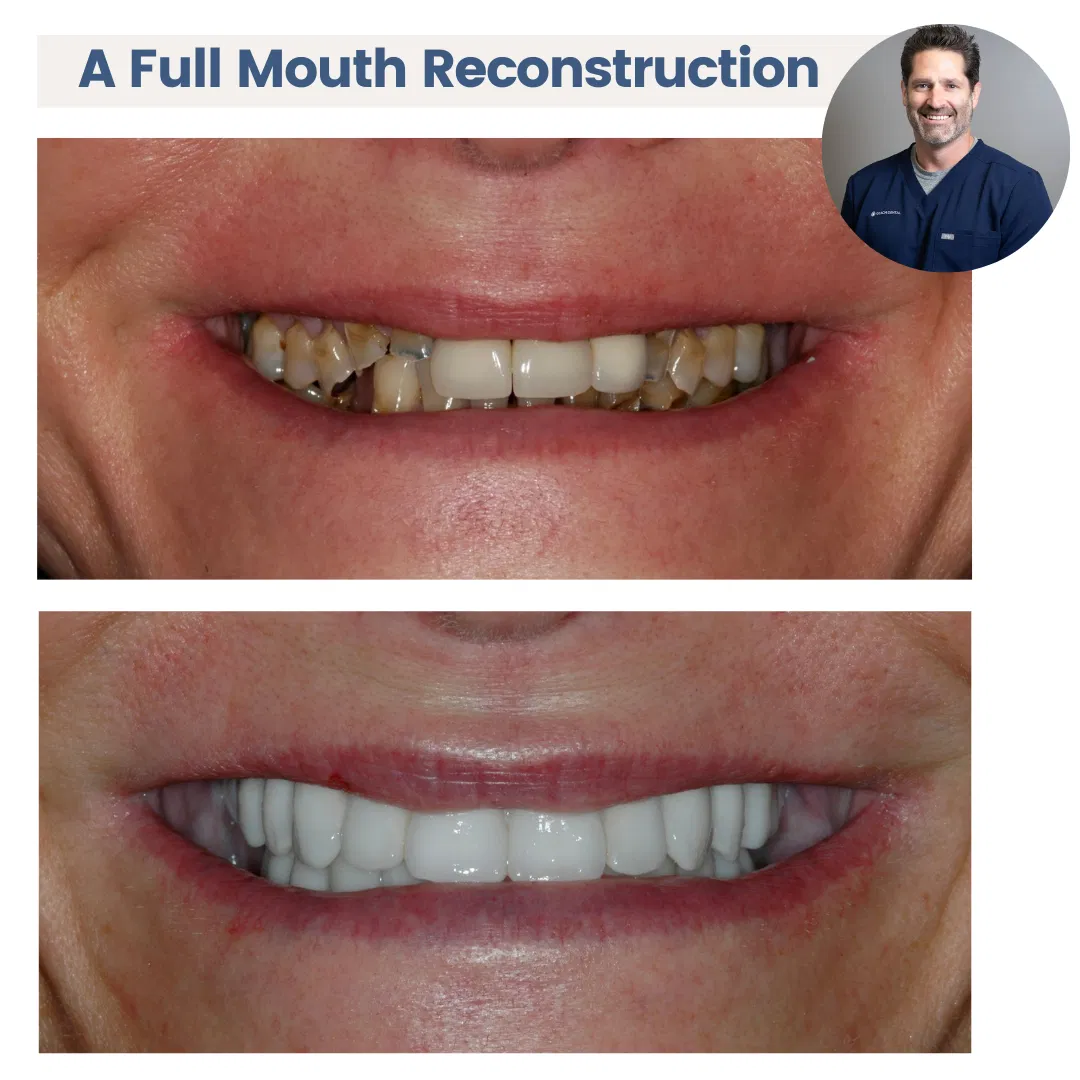
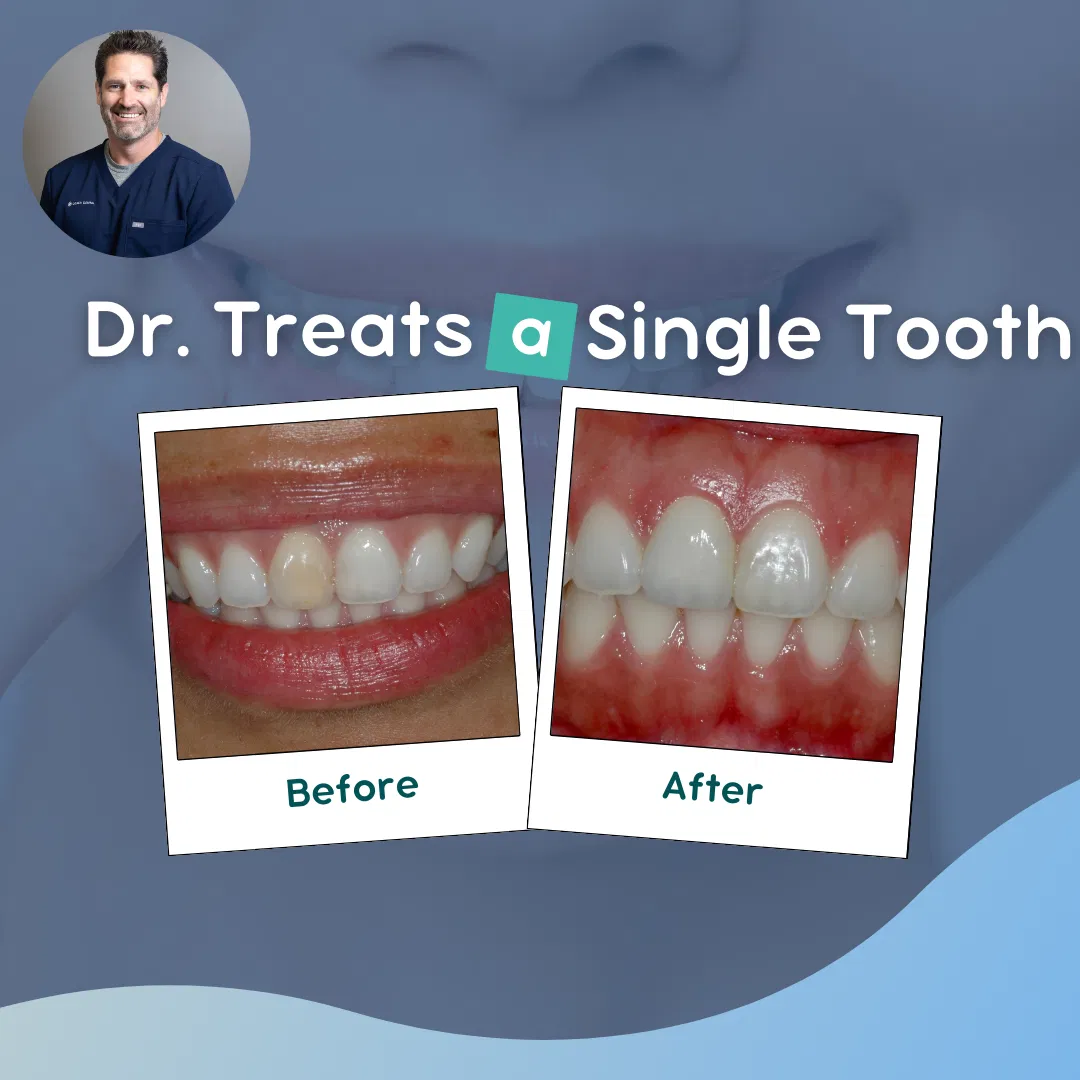
- Customized Crowns: In cases where the existing crown is the root cause of the black border, prosthodontists may recommend a new, precisely fitted crown. This ensures a snug fit and eliminates the risk of future black borders. See case 1 above.
- Material Advancements: Modern crown materials offer superior aesthetics and longevity. All ceramic crown materials such as zirconia are used, for natural-looking and durable results. Having an in-office laboratory technician, where our crowns are fabricated in our office allows us to achieve excellent aesthetic results that match your surrounding teeth.
Gingival Reshaping
- Surgical Procedure: Gingival reshaping, or gum contouring, involves a minor surgical procedure to adjust the gum line. By reshaping the gums to the appropriate level, we can create better harmony and improve the proper aesthetic tooth proportions. New crowns are often needed in conjunction with this surgical procedure to hide the black borders.
Porcelain Veneers
- Thin, Aesthetic Facings: Porcelain veneers are thin ceramic facings that are custom-made to cover the front surface of teeth. They can effectively mask black borders, providing a natural and aesthetically pleasing outcome.
- Minimally Invasive: Veneers require less tooth reduction, helping to preserve the underlying tooth structure.
Composite Bonding
- Resin Application: Composite bonding involves the application of tooth-colored resin to cover the black border area. This resin is skillfully shaped and polished to match the surrounding tooth structure.
- Cost-Effective: Bonding is a cost-effective solution for concealing black borders and enhancing the crown’s appearance.
Prosthodontists employ these treatment options with precision and expertise, tailoring the approach to each patient’s unique circumstances and preferences. Treatment choice depends on factors such as the cause of the black border, the patient’s oral health, and their aesthetic goals.
Recovery and Aftercare
Post-Treatment Care
- Follow Professional Guidance: After any dental procedure, it’s vital to adhere to the specific instructions provided by your prosthodontist. This may include dietary restrictions, oral hygiene practices, and medication as needed.
- Monitor Symptoms: Pay attention to any symptoms such as lingering tooth sensitivity and report any concerns or complications to your prosthodontist promptly.
Long-Term Maintenance
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Scheduling routine dental appointments is crucial for monitoring the health of your crown and gums. Your prosthodontist can detect any issues early and address them promptly.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain excellent oral hygiene by gentle brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash as your prosthodontist recommends. A clean and healthy mouth can reduce the risk of future black borders.
- Avoiding Risk Factors: Be mindful of habits that can contribute to black borders, such as smoking or excessive force on your teeth. Minimizing these risk factors can help preserve your dental restoration.
By following a comprehensive post-treatment care plan and committing to long-term maintenance, you can ensure the longevity and aesthetics of your dental crown while preventing the recurrence of black borders. Your prosthodontist will guide you through the steps to keep your smile healthy and beautiful.
Summary
The presence of a black border around your dental crown can significantly mar your smile’s appearance and erode your confidence. Geach Dental, with two convenient locations in Downtown Los Angeles and Laguna Niguel, Orange County, specializes in resolving this issue. Our prosthodontic team will use advanced knowledge, specialized expertise, and cutting-edge technology to ensure you regain the attractive and confident look you deserve.
We are dedicated to providing every patient with tailored treatment in a comfortable environment. Our commitment includes comprehensive consultations to ensure you fully understand the procedure, its potential challenges, and the rewards it offers. Your satisfaction and comfort are our top priorities.
To take the first step toward eliminating the black border and achieving a healthier, more attractive smile, contact us today at (213) 622-3339 or click here to schedule a consultation. Geach Dental is your trusted partner on the journey to a more radiant and confident smile.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR: Meet Dr. Adam Geach, distinguished prosthodontic specialist and owner of Geach Dental. His dental education includes Harvard School of Dental Medicine and the University of Connecticut, where he earned a D.M.D. and an M.D.Sc. in Prosthodontics, respectively. Dr. Geach holds Diplomate status with the American Board of Prosthodontics, underscoring his exceptional expertise in dental care.
At his clinics in Los Angeles and Laguna Niguel, Dr. Geach offers a wide range of services, from cosmetic treatments to full-mouth reconstructions, all delivered with a focus on personalized patient care.Take the first step toward your ideal smile and improved oral health by clicking here.